How AI agents are revolutionizing digital marketing
Artificial intelligence (AI) agents are set to become your most valuable companions.
AI agents could potentially disrupt Google’s and Amazon’s search functionalities, according to Bill Gates’ latest AI prediction.
This is because AI agents can accomplish desired tasks and goals, communicate, collaborate and solve problems in real-time without human input, delivering information in the desired format faster and more efficiently.
This article covers:
- The nature of AI agents.
- The agentic framework.
- Steps to develop use cases for AI agents.
- How to create an organizational strategy for launching AI agents.
- Methods to measure the impact of AI agents.
What are AI agents?
An AI agent is a software application designed to process data and take actions autonomously to achieve specific goals. It functions similarly to a virtual assistant, collecting data, making decisions and performing actions without direct human intervention.
AI agents solve problems by:
- Analyzing the issue.
- Breaking it down into smaller parts.
- Creating a step-by-step solution.
- Executing these steps.
They then evaluate the outcomes, refine the solution if necessary and repeat the process until they reach the desired result.
AI agents are particularly effective for handling complex, dynamic and iterative tasks, where they interact with multiple systems and respond to user inputs (such as wishes or commands) to achieve their objectives.
For example, an AI agent could autonomously book a flight ticket based on specified criteria.
From a marketing perspective, AI agents can gather user intent signals and data to help you deliver personalized experiences to your audiences.
You can also use AI agents for trip planning and itinerary building. These are just a few of the many ways AI agents can enhance your marketing efforts.
What is the agentic framework?
The agentic framework is a conceptual model or architecture for developing and understanding AI agents.
For example, open-source frameworks like Lang Graph enable developers to create intelligent agents that can understand instructions and take actions autonomously.
An AI framework manages the allocation of necessary computing and memory resources, allowing agents to perform their tasks efficiently.
Each user interaction with an agent (application) initiates a conversation (or thread), which can span over extended periods.
During these conversations, the agent must maintain context (through memory and state management) to provide relevant responses.
Agent frameworks help maintain these contexts independently, even when multiple conversations occur simultaneously.
Additionally, these frameworks enable monitoring of each agent’s operation and performance. They allow control over their behavior, with options to start, stop or modify actions as needed.
For these reasons, selecting the right AI framework is crucial for achieving reliable, high-performance scalability, especially when supporting thousands of users concurrently.
Dig deeper: Does generative AI save time, money and resources in SEO?
Differences between AI agents, chatbots and multiagents
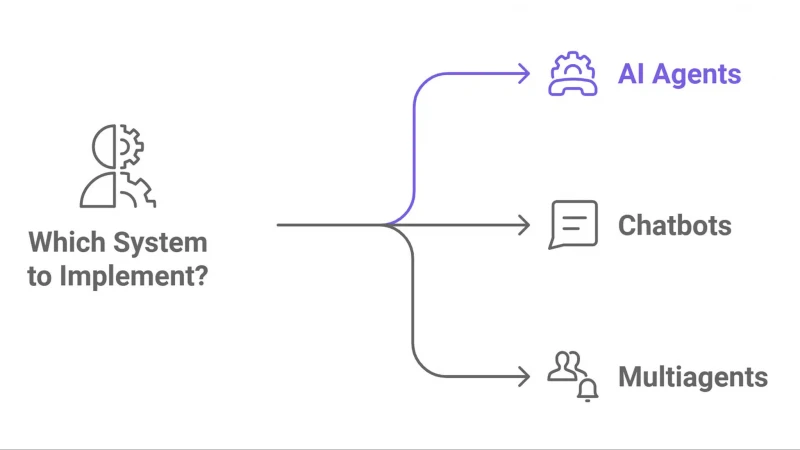
While AI agents, chatbots and multiagents all utilize AI technology, they differ significantly in complexity, functionality and application.
- AI agents: Can autonomously “act” and “think” toward specific goals.
- Chatbots: Systems designed for basic interaction and conversation, offering responses to simple hardcoded questions.
- Multiagents: Advanced AI systems where multiple agents work collaboratively toward a shared goal.
Why do businesses need AI agents and the agentic framework?
By leveraging AI agents, businesses can automate complex, repeatable tasks, improve efficiency and customer experience and scale marketing efforts exponentially.
Use cases for AI agents in digital marketing include:
- Conversational agents.
- Search agents.
- Booking agents.
- Support agents.
- Personalized content creation and curation agents.
- Agents providing insights, market mix modeling, budgeting and forecasting needs.
9-step process for creating agents and agentic framework
Developing effective AI agents and implementing the agentic framework requires a structured approach. Here’s a nine-step guide to get you started.
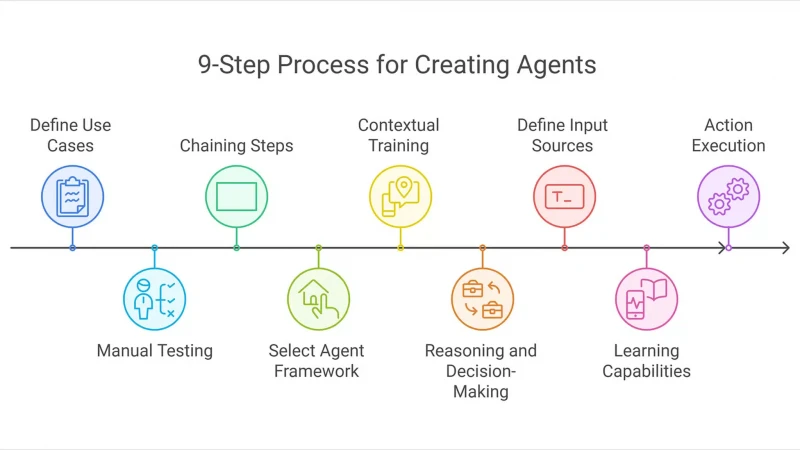
Step 1: Define use cases
- Identify specific problems or tasks for the agent to address within your chosen framework.
Step 2: Manual testing
- Test use cases and the actions agents can take manually to ensure each step works as expected.
Step 3: Chaining steps
- Ensure all necessary steps are properly sequenced to enable the agent or multi-agent system to function effectively.
Step 4: Select agent framework
- Decide which agent framework best suits your needs once use cases are established.
Step 5: Contextual training
- Provide contextual information to the agent, using memory components to maintain context across interactions.
Step 6: Reasoning and decision-making
- Implement processes for the agent to analyze information, make inferences and develop plans of action.
Step 7: Define input sources
- Determine the framework and specify all sources of input for the agents.
Step 8: Learning capabilities
- Equip the agent with learning capabilities to improve performance based on past experiences, leveraging machine learning techniques.
Step 9: Action execution
- Design the execution of decisions through effectors or outputs to enable effective interaction with the environment.
In an agent-driven economy, advertisers will likely shift toward offering more discounts and special offers instead of traditional advertisements like text, images and rich media.
There are several ways to measure the value of agents, from saving time to improving quality and accuracy and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Caveats of using AI agents
Businesses thinking about deploying AI agents must understand the following caveats:
- Agents are not everyone: Wherever human interaction is required, AI agents might cause poorer customer experience than improving them. (Think hospitality and healthcare.)
- Agents require lots of data: For agents to be effective, significant amounts of data must be made available to them. Lower-quality content or poor data might make them ineffective and can produce weaker results.
- Agents need SaaS 2.0 infrastructure: AI agents will require SaaS 2.0 infrastructure and data consolidation across various disparate data sources. Deploying agents with existing infrastructure is still possible but will lead to a poor experience.
The future of AI-driven digital marketing
The digital marketing landscape is rapidly evolving, with AI agents poised to lead the charge.
The focus is shifting toward agents that excel in reasoning and can take meaningful actions on behalf of users, as highlighted by Sundar Pichai at this year’s Google I/O. This technological leap presents an incredible opportunity for marketers.
By leveraging AI agents and the agentic framework, businesses can automate repetitive and predictable tasks, freeing up valuable resources to focus on strategy and creativity.
These agents are not just tools for efficiency; they represent a fundamental transformation in how brands interact with customers, deliver personalized experiences and drive growth.
The rise of AI-driven marketing underscores the need for organizations to adapt and innovate, ensuring they remain competitive in a dynamic and agent-driven digital economy.
As we move forward, embracing these advancements will be key to unlocking new levels of marketing effectiveness and customer engagement.
Dig deeper: The billion-dollar one-person SEO agency: Fiction or the future?